Vuex工作原理
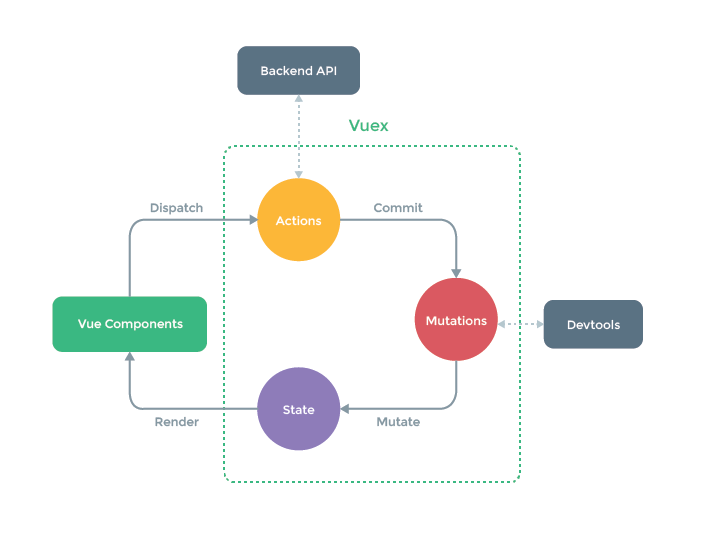
Vuex三个重要工作区域
Actions
在Vue Components调用dispatch()要至少传两个传输,第一个参数为object对象,为在Actions中想要调用的函数名称,第二个参数为想要传递的数据。逻辑运算由Actions来进行,可以减少代码的冗余和增加复用性。在Actions可以调用后端接口或发ajax请求等操作,可以处理业务逻辑。在Actions获得的第一个参数为context可以在context调用commit等方法。尽量不要在Actions修改state中数据,Devtools捕捉不到行为
Mutations(方法名一般为大写,方便与Actions区分)
在Vue Components或Actinos中调用commit()要至少传两个传输,第一个参数为object对象,为在Mutations中想要调用的函数名称,第二个参数为想要传递的数据。此时Mutations所要调用的第一个值为整个state,第二个则为传递过来的数据,在Mutations中调用state里的参数会自动进行调用Mutate函数将State数据进行变换。函数内部需要return
State
state主要存放数据,State中数据改变Vuex会主动调用Render对组件重新进行渲染。
其他配置项
getters
类似于vue中的computed属性,在getters中调用时可以获取到state中的相关数据。适合逻辑复杂并且需要复用的数据。
mapState
可以直接从state中拿数据,增加效率,一般以扩展运算符...形式放在computed中
//在要使用state的组件中的computed调用
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
//注册完毕后可以直接使用插值语法
computed:{
//对象写法,因为后方必须带引号无法使用对象简写方式
...mapState({example:'example1',example2:'example2'})
//数组写法,生成的计算属性名和读取的数据名一致
...mapState(['example1','example2'])
}mapGetters
同上,可以直接从getters中拿数据,增加效率,一般以扩展运算符...形式放在computed中
//在要使用state的组件中的computed调用
import {mapGetters} from 'vuex'
//注册完毕后可以直接使用插值语法
computed:{
//对象写法,因为后方必须带引号无法使用对象简写方式
...mapGetters({example:'example1',example2:'example2'})
//数组写法,生成的计算属性名和读取的数据名一致
...mapGetters(['example1','example2'])
}mapMutations
可以不用自己在方法中使用commit来调用Actions
//在要使用state的组件中的methods调用,调用的时候需要传参,要是没有传参会传所触发的事件事件
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
methods:{
//接入mapMutations生成对应方法,方法中会调用commit去联系Mutations
//对象写法
...mapMutations({example:'example1',example2:'example2'})
//数组写法
...mapMutations(['example1','example2'])
}mapActions
可以不用自己在方法中使用commit来调用Actions
//在要使用state的组件中的methods调用,调用的时候需要传参,要是没有传参会传所触发的事件事件
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'
methods:{
//接入mapActions生成对应方法,方法中会调用dispatch去联系mapActions
//对象写法
...mapActions({example:'example1',example2:'example2'})
//数组写法
...mapActions(['example1','example2'])
}Vuex工作环境(Vue2版本)
目前使用npm i vuex安装的是Vue3版本的Vuex
使用npm i vuex@3才能安装Vue2版本的Vuex
安装完成后在根目录创建store文件夹,并创建index.js
//该文件用于创建Vuex最为核心的store
//引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
//引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
//准备actions 用于相应组件中的动作
const actions = {}
//准备mutations 用于操作数据
const mutations = {}
//准备state 用于存储数据
const state = {}
//准备getters 用于将state中的数据进行加工
const getters = {}
//创建store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
getters
})
//暴露store
export default store注意:import语句会优先执行,Vue.use(Vuex)在main.js中使用会报错
//在vue-cli根目录的main.js中引入Vuex,这样可以全局使用vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//引入store
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el:'#app',
render: h => h(app),
store
})Vux模块化
//该文件用于创建Vuex最为核心的store
//引入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
//引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//使用Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
//将功能进行模块化封装,可以封装在其他js文件中
const example1 = {
//想要直接读取数据需要开启命名空间,默认为false
namespaced:true,
actions:{},
state:{},
getters:{},
mutations:{}
}
const example2 = {
//想要直接读取数据需要开启命名空间,默认为false
namespaced:true,
actions:{},
state:{},
getters:{},
mutations:{}
}
//创建store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
//在store.state会存放除getters外的方法
example1,
example2
}
})
//暴露store
export default store